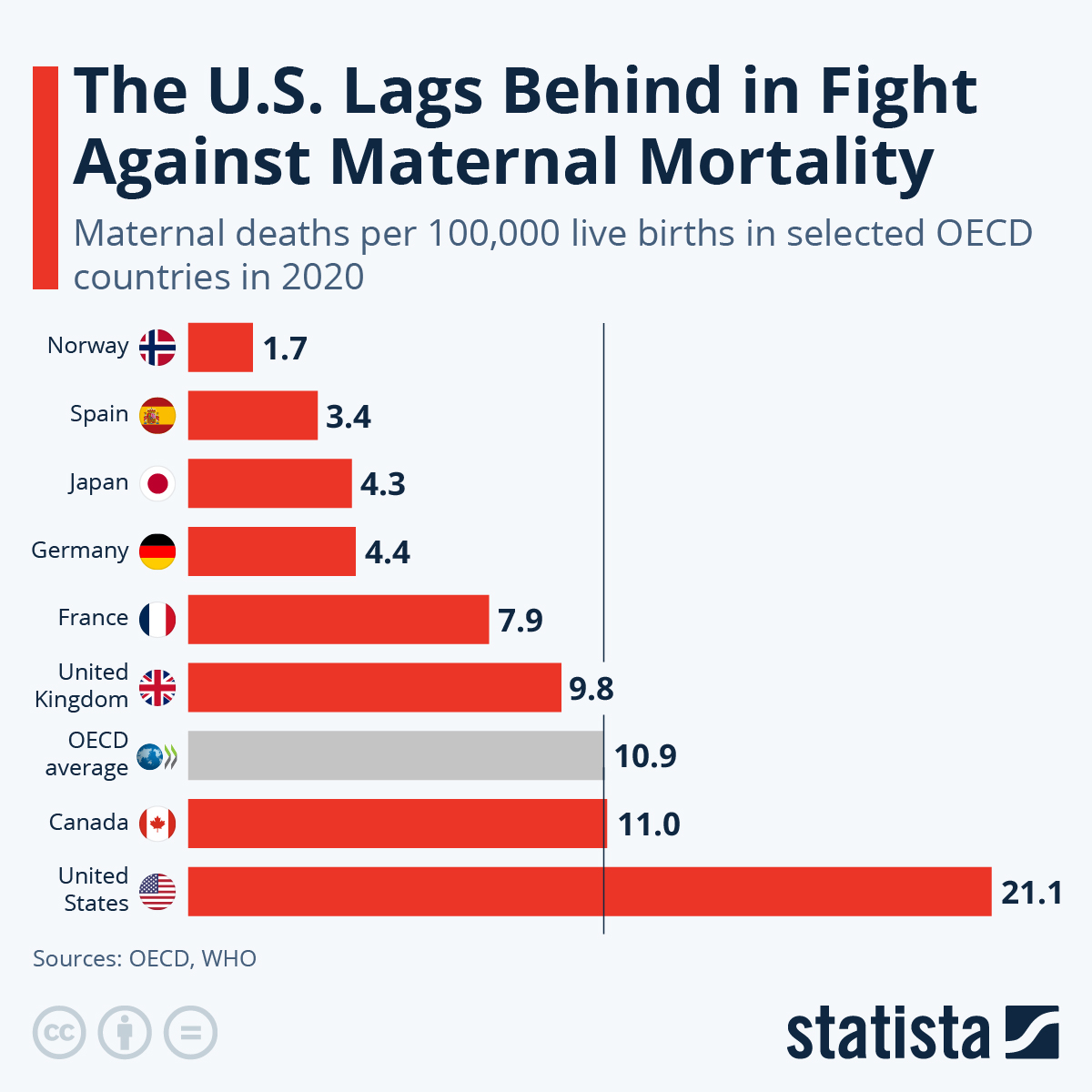
Maternal mortality remains a pressing concern in the U.S., where pregnancy-related deaths have become alarmingly high compared to other high-income countries. Despite substantial advancements in healthcare, the country continues to grapple with preventable maternal fatalities, with over 80% of these tragedies being avoidable. Recent studies have showcased that disparities in U.S. maternal health are deeply intertwined with race and geography, as certain populations face far higher risks. In fact, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience maternal mortality rates nearly four times that of their white counterparts. It is crucial to address the systemic issues contributing to this public health crisis, including improving prenatal care and enhancing postpartum support to mitigate these devastating statistics and ensure safer outcomes for all mothers.
The issue of maternal mortality, often recognized as the rate of death associated with childbirth, poses a significant public health challenge in the United States. Within this context, pregnancy-related fatalities are rising, highlighting an urgent need for improvement in maternal health services. This situation is exacerbated by various factors such as inadequate postpartum care and stark racial disparities affecting effective healthcare access and quality. Furthermore, chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease during pregnancy have emerged as leading causes of these adverse outcomes. Addressing these critical elements will be essential in reversing the trend of increasing maternal deaths and ensuring comprehensive care for mothers throughout their pregnancy journey.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. continue to be a major public health concern, especially as they remain the highest among high-income countries. According to recent research conducted by the National Institutes of Health, the United States has seen a troubling increase in pregnancy-related deaths from 2018 to 2022. This alarming trend underscores the need for systemic improvements in maternal healthcare, including better prenatal care and longer postpartum monitoring. The study highlights that over 80% of these deaths are preventable, calling into question the efficacy of current healthcare practices surrounding pregnancy and childbirth.
A critical factor contributing to these striking rates is the diverse healthcare landscape across the country, often characterized by inequities and regional disparities. Different states exhibit varying maternal mortality rates, influenced by factors such as access to care and the level of support available for new mothers. This inconsistency poses the question of how certain states, like California, have successfully lowered their rates and what other states can learn from their approaches. Policymakers must focus on creating a cohesive strategy that addresses these disparities to achieve better maternal health outcomes nationwide.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial disparities in maternal health outcomes have persisted in the U.S., with significant differences in maternal mortality rates among various ethnic groups. The recent study revealed that American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Non-Hispanic Black women also experience disproportionately high rates. These statistics reflect a larger issue of systemic inequities that affect the health outcomes of marginalized communities, emphasizing the urgent need for targeted interventions and policies aimed at bridging the gap.
Addressing these racial disparities requires a multifaceted approach, including enhancing the quality of care provided to pregnant women of color and increasing accessibility to prenatal services. It also involves implementing cultural competency training among healthcare providers to minimize bias and discrimination within medical settings. By understanding and addressing the root causes of these disparities, we can work towards creating a more equitable maternal health system that ensures all women receive the care they need regardless of their racial or ethnic background.
The Importance of Postpartum Care
Postpartum care plays a crucial role in maternal health, yet it is often insufficiently prioritized within the healthcare system. The recent findings show that nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur during the postpartum period, highlighting the necessity for extended care beyond the traditional six-week postpartum check-up. As the healthcare landscape evolves, it is becoming increasingly clear that the journey to recovery extends far beyond the immediate aftermath of childbirth. Improved postpartum care can help identify health complications early and provide ongoing support to new mothers.
Innovative solutions are needed to reshape the approach to postpartum care, ensuring it is comprehensive and patient-centered. This includes routine screenings for chronic conditions such as hypertension, which have been linked to increased mortality rates. Strengthening postpartum support services can not only reduce maternal mortality but also enhance the overall well-being of mothers during this critical phase. By recognizing the postpartum period as a vital component of the maternal health continuum, we can better foster long-term health outcomes for mothers and their infants.
The Rising Influence of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy
Cardiovascular disease has become a leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States, accounting for over 20% of fatalities during and after childbirth. Recent studies emphasize a notable shift from hemorrhage to cardiovascular complications as the primary health concern for pregnant women. This trend has ominous implications, particularly as it has been observed that chronic conditions like hypertension are appearing more frequently among women of childbearing age. Understanding the link between cardiovascular health and pregnancy is critical for developing targeted interventions.
As cardiovascular conditions can lead to severe complications during pregnancy, healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring at-risk patients. Early identification and management of these conditions can significantly impact maternal health outcomes. Continuous education and awareness campaigns about the importance of cardiovascular health before, during, and after pregnancy are essential. By prioritizing the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease in this population, we can work toward reducing the stark maternal mortality rates that continue to plague the U.S.
Impact of COVID-19 on Maternal Health Trends
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated existing challenges in maternal healthcare, leading to a noticeable increase in pregnancy-related deaths during the early years of the pandemic. The data shows a sharp uptick in mortality rates in 2021, a trend that raised alarms among public health officials and healthcare providers. As the healthcare system faced unprecedented pressures and disruptions, access to essential services for pregnant women may have been compromised, leading to detrimental health outcomes.
Post-pandemic recovery strategies must prioritize maternal health to address the negative impacts experienced during this period. This includes ensuring women receive timely prenatal care and strengthening the support systems available for postpartum recovery. By learning from the lessons of the pandemic and implementing robust healthcare reforms, we can foster a safer environment for expecting mothers and reduce the risk of preventable pregnancy-related deaths in the future.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure
To tackle the rising rates of maternal mortality effectively, there is an urgent need for enhanced investment in public health infrastructure. This encompasses everything from improving access to quality prenatal and postpartum care to implementing comprehensive tracking systems for maternal health outcomes. The current public health landscape is at risk due to budget cuts and a deprioritization of maternal health initiatives, which could hinder efforts to improve care and outcomes for mothers and infants.
Strategic investments must be made not only in healthcare facilities but also in community-based programs that support women throughout their reproductive journey. Strengthening public health infrastructure will enable healthcare providers to ride the wave of innovation and implement best practices in maternal care. Collaborative efforts at the state and federal levels can open doors to sustainable solutions that will ultimately lead to decreased mortality rates and improved overall maternal health.
Policy Changes Needed to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
Changes in policies and healthcare practices are imperative to combat the startling rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. The study highlights the need for a standardized approach to maternal health that addresses the disparities observed across different states and communities. Policymakers must prioritize initiatives that promote equitable access to high-quality prenatal and postpartum care, focusing on the implementation of best practices that have successfully lowered mortality rates in some regions.
Addressing maternal health outcomes also requires a thorough understanding of the social determinants of health, which contribute to disparities in care. Policymakers should advocate for policies that mitigate the impact of systemic inequities, such as those related to race and socioeconomic status. By fostering an inclusive and equitable healthcare landscape, the U.S. can hope to reduce maternal mortality rates and ensure that all women receive the quality care they deserve.
Innovative Solutions for Improving Maternal Healthcare
Harnessing innovative approaches and technological solutions must become a priority in improving maternal healthcare. This can include telehealth options for prenatal and postpartum check-ups, allowing increased access for women who may face transportation or mobility challenges. Additionally, utilizing data analytics to track and analyze maternal health outcomes can help identify trends, target interventions, and improve care delivery mechanisms.
Furthermore, integrating community resources and support systems that empower women to take charge of their health can lead to more favorable outcomes. Programs that educate expecting mothers on recognizing warning signs of complications and fostering peer support networks can greatly enhance the maternal healthcare experience. A proactive approach to maternal health using innovative solutions can help bridge gaps in care, ultimately leading to reductions in maternal mortality.
The Role of Education in Maternal Health Awareness
Education and awareness around maternal health are vital to reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Providing comprehensive education on prenatal care, the importance of addressing chronic conditions, and recognizing the signs of complications can empower women to seek timely medical assistance. Public health campaigns aimed at raising awareness about maternal health issues can play an essential role in informing women of their rights and the resources available to them.
Moreover, engaging healthcare providers in continuous training programs can help address biases and improve communication with patients. Educators and healthcare professionals must work together to create informative resources that cater to the unique cultural and social needs of diverse communities. Improved education and awareness are critical components of addressing the pressing challenges of maternal mortality and ensuring that every mother has access to the care she deserves.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
The primary causes of maternal mortality in the U.S. include cardiovascular diseases, which account for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. Other significant causes are hemorrhage, hypertension, and postpartum complications. Chronic conditions affecting pregnant individuals, such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease, are increasingly impacting maternal mortality rates.
Why are racial disparities in maternal mortality rates significant?
Racial disparities in maternal mortality rates are significant because they highlight systemic inequities in U.S. maternal health. American Indian and Alaska Native women experience mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women. This emphasizes the need for targeted interventions to improve healthcare access and quality for underrepresented racial groups.
How can postpartum care impact maternal mortality rates?
Effective postpartum care is crucial for reducing maternal mortality rates. Many pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after delivery. Addressing postpartum health as a continuum, rather than a set period, can improve outcomes by providing continuous support for conditions such as hypertension and mental health.
What role does chronic disease play in U.S. maternal mortality?
Chronic diseases, especially cardiovascular conditions like hypertension, are increasingly affecting pregnant individuals at younger ages, contributing significantly to maternal mortality. As the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, addressing these chronic conditions is vital for reducing the overall risk associated with pregnancy.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates continuing to rise. This alarming statistic indicates that more than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, underscoring the need for improved healthcare systems and policies to enhance maternal health.
What steps can be taken to reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
To reduce pregnancy-related deaths, it is essential to invest in public health infrastructure, improve access to comprehensive maternal healthcare, address systemic inequities, and implement quality improvement initiatives in prenatal and postpartum care. Recognizing the importance of sustained healthcare beyond the first few weeks after delivery is critical.
How do societal factors influence maternal mortality rates?
Societal factors such as healthcare access, economic stability, and education significantly influence maternal mortality rates. Disparities in these factors often result in unequal healthcare delivery, making certain populations more vulnerable to pregnancy-related deaths.
What is the significance of late maternal deaths in understanding maternal mortality?
Late maternal deaths, which occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, represent a substantial and often overlooked portion of maternal mortality. Recognizing this timeframe’s importance can lead to better healthcare systems that support continuous maternal care and address complications that arise after childbirth.
What does the rise in maternal mortality rates during the COVID-19 pandemic indicate?
The rise in maternal mortality rates during the COVID-19 pandemic indicates that public health emergencies can exacerbate existing health disparities and result in adverse outcomes for pregnant individuals. This highlights the need for robust maternal health strategies that can withstand challenges posed by crises.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates continuing to rise from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. |
| Preventability | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant differences in mortality rates exist among racial groups, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Aging Factors | The leading cause of pregnancy-related death has transitioned to cardiovascular disease, especially affecting middle-aged women aged 25 to 39. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and 1 year postpartum, indicating a need for ongoing care beyond traditional timelines. |
| Public Health Investment | Continued investment in public health infrastructure is essential to improve maternal health outcomes and reduce pregnancy-related deaths. |
Summary
Maternal mortality remains a critical issue in the United States, where it leads the way among high-income nations. Despite efforts to combat this growing crisis, the country is witnessing alarming trends in pregnancy-related deaths, primarily due to a combination of healthcare access disparities, persistent systemic inequities, and insufficient prenatal and postpartum care. Strategies focused on enhancing public health infrastructure and addressing the specific needs of diverse racial groups are essential to reversing this trajectory and ensuring healthier pregnancies for all women.