Alzheimer’s early detection is becoming increasingly vital in the fight against cognitive decline, particularly as researchers unveil innovative methods for identifying those at risk long before notable symptoms manifest. A recent study from Mass General Brigham highlights how olfactory tests, which assess the ability to recognize and remember odors, can serve as a powerful screening tool for Alzheimer’s disease. These tests can conveniently be conducted at home, providing a non-invasive, cost-effective solution for families concerned about cognitive impairment. Notably, older adults displaying signs of olfactory dysfunction often demonstrated lower scores on these tests, marking them as potential early indicators of Alzheimer’s. This breakthrough not only paves the way for timely diagnosis but also opens avenues for early intervention and treatment in the battle against Alzheimer’s disease.
The quest for recognizing early signs of Alzheimer’s involves exploring various indicators of cognitive decline, including methods to assess memory and sensory functions. Cognitive impairment, often manifested through difficulties in memory recall and recognition, is one of the primary concerns in older populations. Studies focused on olfactory dysfunction suggest that the loss of smell might be an early warning sign, indicating potential neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, advancements like the home test for Alzheimer’s highlight the importance of accessible screening tools in everyday settings. By leveraging simple tests that can identify these subtle signs, researchers aim to improve early detection of Alzheimer’s disease and enhance the overall quality of life for those affected.
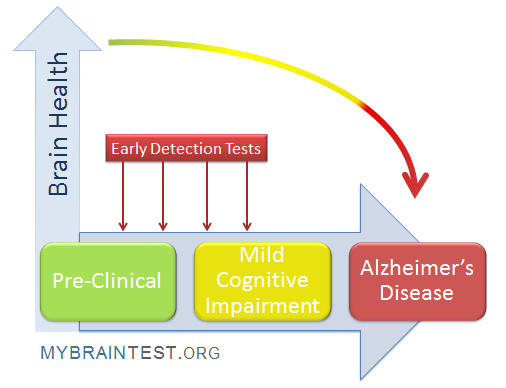
Revolutionizing Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Alzheimer’s early detection is critical in managing the progression of cognitive impairment. Recent advances in research have highlighted the potential of olfactory testing as an innovative approach to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease significantly earlier than traditional methods. By leveraging the connection between the sense of smell and cognitive functions, researchers at Mass General Brigham have developed an at-home olfactory test to help identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s. This allows for early intervention strategies that could slow down the disease’s progression, a vital step given that many patients do not see symptoms until the disease is in advanced stages.
The implications of this early detection are enormous. Not only can it help in potentially mitigating the effects of Alzheimer’s, but it also opens up further research avenues into the neurological basis of cognitive impairment. By implementing olfactory dysfunction assessments widely, clinicians could refine their understanding of Alzheimer’s onset. This kind of innovation in the diagnostic process is crucial as it provides both patients and healthcare systems with valuable time to prepare and act accordingly.
Understanding Olfactory Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Olfactory dysfunction, defined as the reduction or loss of the sense of smell, has emerged as a significant early indicator of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Studies show that individuals experiencing olfactory dysfunction often exhibit cognitive impairment long before memory loss becomes apparent. This correlation underlines the importance of smell tests as part of broader cognitive screenings for older adults. Researchers aim to validate these findings through regular assessments, potentially empowering patients with early interventions that can hasten treatment plans or lifestyle changes.
Incorporating olfactory tests into routine cognitive assessments could dramatically change how we approach neurodegenerative disease prevention. Not only do these tests provide an easily administered and non-invasive method for screening, but they also support earlier, more precise interventions for those at risk of Alzheimer’s disease. As understanding of the olfactory function deepens, it may help shed light on the underlying mechanisms that cause cognitive decline, guiding future therapies.
The Home Test for Alzheimer’s: A Game Changer
The introduction of an at-home test for Alzheimer’s represents a monumental shift in how detection occurs on an individual level. This simple polling of smell perception is not just cost-effective; it democratizes access to crucial early detection methods for cognitive impairment. Older adults, who might struggle with transportation to clinics or hospitals, can now conduct this test in the comfort of their home, making it accessible to a much wider range of individuals.
Additionally, the home test emphasizes the importance of proactive health monitoring. By encouraging regular assessments of cognitive function via olfactory testing, individuals can take charge of their brain health earlier. This shift towards personal responsibility in health management is critical for increasing early intervention success rates and ensuring better long-term outcomes for those identified as at risk for Alzheimer’s.
The Role of Scientific Research in Alzheimer’s Detection
Scientific research plays a pivotal role in advancing methods of Alzheimer’s early detection. The power of olfactory testing, as demonstrated by recent studies from Mass General Brigham, highlights how innovative research can translate into practical, real-world applications. With funding from organizations like the National Institutes of Health, researchers are continually exploring the connections between various sensory functions and cognitive decline, identifying new biomarkers that could reshape diagnostic criteria.
Moreover, ongoing research allows for the continuous improvement of test methodologies and understanding of Alzheimer’s pathology. Findings from the olfactory testing studies are expected to evolve, paving the way for integrated approaches that combine sensory tests with other cognitive assessments. As more researchers validate these techniques, the potential for developing new tools and therapies to combat Alzheimer’s will exponentially increase.
Cognitive Impairment: Detecting Symptoms Earlier
Detecting cognitive impairment earlier is essential for effective intervention. The link between cognitive decline and olfactory dysfunction emphasizes the need for continued awareness and education regarding Alzheimer’s disease. The earlier we can identify at-risk individuals through simple tests like olfactory assessments, the sooner we can implement lifestyle changes or begin preventative therapies to preserve cognitive health.
Awareness about cognitive impairment not only assists in Alzheimer’s early detection but also encourages individuals to take their brain health seriously. Understanding these early warning signs can lead to increased collaboration between patients and healthcare providers to create tailored health plans designed to maintain mental acuity as individuals age.
Advancements in Alzheimer’s Research: The Future Looks Bright
The promising advancements in Alzheimer’s research signal a bright future in the realm of cognitive health management. Scientists are continually uncovering relationships between different sensory functions and neurodegenerative diseases. As observed with olfactory testing, innovative research methodologies are paving new pathways for early detection and intervention, representing a hopeful step towards eventually finding a cure for Alzheimer’s.
As research progresses, it is anticipated that combining various testing techniques will provide even more robust predictive tools for Alzheimer’s. Consequently, the healthcare community is urged to invest in multidimensional approaches that consider personal health, genetics, and lifestyle factors, which will enable tailored, effective responses to cognitive impairment.
The Importance of Early Intervention in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Early intervention in Alzheimer’s treatment is crucial for improving outcomes for those diagnosed with cognitive impairment. By identifying the symptoms of Alzheimer’s early on, healthcare providers can implement strategies aimed at slowing disease progression. Utilizing tests like the olfactory assessment enables healthcare professionals to create individualized treatment plans, which may include cognitive therapies, lifestyle changes, or pharmacological treatments.
Furthermore, early detection allows families to adjust and prepare for future care needs, potentially alleviating stress as the disease progresses. Awareness and education about early cognitive symptoms not only empower patients but also their loved ones to make proactive decisions regarding treatment and lifestyle adjustments that can also mitigate the impact of Alzheimer’s.
Community and Support Networks for Alzheimer’s Patients
The impact of Alzheimer’s extends beyond the individual, creating a ripple effect through families and communities. Establishing strong community support systems is vital in promoting Alzheimer’s early detection and fostering environments where patients and caregivers feel supported. Community organizations play a critical role in raising awareness, providing resources, and facilitating support groups for those affected by Alzheimer’s.
By creating open lines of communication within community networks, individuals can share insights and strategies for managing the challenges associated with Alzheimer’s. These networks can empower patients to seek earlier intervention and provide caregivers with the necessary resources to support their loved ones effectively. Ultimately, communities can foster resilience and hope amid the challenges brought about by Alzheimer’s disease.
Navigating the Future of Alzheimer’s Research
The future of Alzheimer’s research is filled with promise and opportunity, especially with the development of new diagnostic tools such as olfactory testing. By positioning research at the forefront of Alzheimer’s advocacy, scientists are laying the groundwork for breakthroughs in understanding and treating this devastating disease. Future studies focusing on olfactory functions may lead to novel treatments or preventative measures that could significantly alter the course of Alzheimer’s.
Importantly, as research continues to evolve, the integration of patient feedback into clinical trials will be pivotal. By incorporating patient experiences and outcomes into research agendas, scientists can ensure that new tests and treatments are both effective and practical. This patient-centered approach is likely to improve adherence to early detection protocols and will consequently enhance opportunities for timely interventions in Alzheimer’s disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of Alzheimer’s early detection?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial as it allows for timely interventions that may slow cognitive decline and improve quality of life. Identifying cognitive impairment before memory symptoms appear can lead to proactive care strategies and research opportunities.
How does an Alzheimer’s test help in detecting cognitive impairment?
An Alzheimer’s test, such as the olfactory test developed by researchers, can effectively identify changes in a person’s ability to recognize and remember odors. Lower scores in these tests may indicate early signs of cognitive impairment linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
Can olfactory dysfunction indicate early signs of Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, olfactory dysfunction has been found to serve as an early warning sign for Alzheimer’s disease. The loss of smell can be an overlooked indicator of cognitive decline, helping in the early detection of conditions like Alzheimer’s.
What is the Aromha Brain Health Test and its role in Alzheimer’s early detection?
The Aromha Brain Health Test is a home-based olfactory assessment used to evaluate an individual’s ability to identify and remember scents. This test plays an important role in Alzheimer’s early detection by potentially identifying at-risk individuals before they show significant cognitive symptoms.
Are home tests for Alzheimer’s effective in early detection?
Home tests for Alzheimer’s, including olfactory tests, have shown effectiveness in identifying cognitive impairment. These non-invasive, easy-to-administer tests can help individuals monitor their brain health and detect early signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
What cognitive issues can be associated with Alzheimer’s early detection?
Cognitive issues associated with Alzheimer’s early detection may include memory concerns, difficulty in recognizing odors, and changes in smell identification. These indicators can help signal potential early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
Who should consider taking an Alzheimer’s test for early detection?
Individuals experiencing subjective cognitive complaints, such as memory concerns, or who have a family history of Alzheimer’s should consider undergoing an Alzheimer’s test for early detection. This proactive step can facilitate timely intervention.
How are olfactory tests conducted for Alzheimer’s early detection?
Olfactory tests for Alzheimer’s early detection typically involve participants sniffing odor labels on a card to assess their ability to identify and remember scents. This can be done at home, making it accessible for older adults.
What research supports the use of olfactory tests for Alzheimer’s early detection?
Recent studies published in Scientific Reports have supported the use of olfactory tests in identifying cognitive impairment among older adults. Research led by Mass General Brigham confirmed that these tests can be reliable indicators of Alzheimer’s disease risk.
What role do neuropsychological assessments play in Alzheimer’s early detection?
Neuropsychological assessments complement tests like the olfactory test in Alzheimer’s early detection by providing a comprehensive evaluation of cognitive functions. They help track cognitive decline over time, aiding in understanding the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Institution | Mass General Brigham (affiliated with Harvard) |
| Test Type | Olfactory test to assess smell discrimination and identification |
| Participants | English and Spanish speakers with cognitive complaints |
| Findings | Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower than cognitively normal peers |
| Importance of Early Detection | Could identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s years before symptoms appear |
| Future Research | Testing olfactory dysfunction as a warning sign for neurodegenerative diseases |
| Funding | Supported by the National Institutes of Health |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial for identifying individuals at risk before significant memory symptoms manifest. Recent research by Mass General Brigham highlights an innovative olfactory test, which assesses the ability to discriminate, identify, and remember odors as a potential early warning sign for Alzheimer’s disease. By utilizing simple at-home tests, researchers aim to enhance early detection methods and fundamentally change how we approach treatment for Alzheimer’s, ensuring timely interventions.